Properties: Characteristics of the matter.
Volume: It is the space that an object occupies.
Mass: It is the amount of matter there is in an object.
Solubility: It is the ability to dissolve into another substance.
Conductivity: It is how easy it is for the electricity to pass through a material.
Elasticity: It is the ability to be stretched and then return to its original shape.
Magnetism: It is an invisible force that causes objects to attract or repel one another. Magnets.
Heat: It is energy that can transfer from one matter to another. The hotter matter heats the colder one until the temperature is the same.
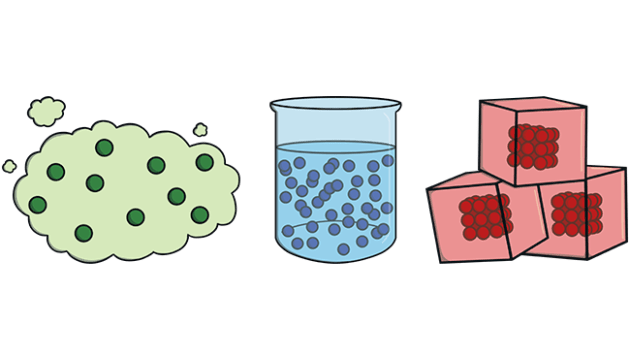
States of matter: Matter can be in three different states: Solid, liquid or gas.
Liquid: It doesn’t have its own shape but keeps the same volume. It adapts to the container that it is in.
Solid: It has its own shape. It always has the same volume because the shape doesn’t change.
Gas: It doesn’t have the same shape and doesn’t keep the same volume. We can reduce its volume if we compress it.
Condensation: It is when a gas change into liquid. It needs to be cooled.
Mixture: It contains two or more substances.
Pure substance: It contains one substance.
Homogenous: A mixture in which we cannot distinguish its components.
Heterogenous: A mixture in which we can distinguish its components
Distillation: This method separates homogeneous mixtures into two liquids. The mixture is heated, the first liquid to evaporate condenses in a cold tube.
Filtration: This method separates heterogeneous mixtures of a liquid and a solid. The mixture goes through a filter that removes the solid.
Evaporation: This method separates homogeneous mixtures of a liquid and a solid. The mixture is heated until the liquid evaporates.
Decantation: This method separates heterogeneous mixtures of two liquids. The heavier liquid is at the bottom and comes out first when you open the tap.
Reversible: Matter that returns to its original state.
Irreversible: Matter that doesn’t return to its original state.